 Around the world there has been an unprecedented explosion in the number of people being infected by tick borne diseases..
Around the world there has been an unprecedented explosion in the number of people being infected by tick borne diseases..
Ticks are very small and live on the blood from pets, farm and wild animals but they can also bite humans who pass through their living environment.

Tick bites are not dangerous in themselves. However, some ticks are infected with bacteria, viruses or parasites that can cause serious diseases in humans so there is a risk that these ticks may pass on their infection to you as they feed on your blood.

Ticks are often found present in long grass
In Europe a tick-borne disease to be aware of is Lyme borreliosis which can occur in areas where infected ticks that transmit the disease are found. Ticks thrive in shady and humid woodland, clearings with grass, open fields and bushes. They live in both rural and urban locations.

Ticks’ life cycles go through four stages: egg, larva, nymph and adult. During the last three stages the tick may bite and can transmit disease.
To the naked eye the larvae look like specks of dust, while nymphs are slightly larger, pinhead or poppy seed size. Adult ticks have eight legs and are the size of small spiders. The adult ticks can also vary in colour, from reddish to dark brown or black. Once fed, a female tick can grow to the size of a pea, as its body fills with blood.
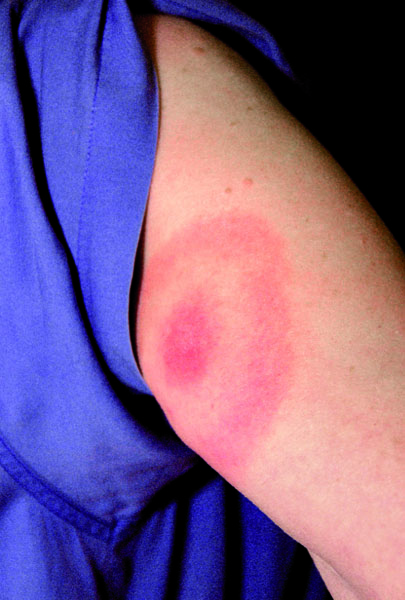
Reddish skin rash in a ring around the bite
Lyme borreliosis
If you have been bitten by a tick and you experience any of the following symptoms within 30 days after the bite, please contact your doctor as you may have contracted Lyme borreliosis:
• Reddish skin rash in a ring shape around the bite
• Flu-like symptoms such as fever, tiredness, headache

People active in the out doors should regularly check themselves for ticks..
Most cases of Lyme borreliosis can be treated successfully with a few weeks of antibiotics. However, if left untreated, the disease can in the later stages infect the heart, joints and nervous system.
Preventive measures
There is no vaccine against Lyme borreliosis, so tick awareness, using insect repellents on your skin and clothes (clothes specific insect repellents should not be used on the skin) and protective clothing in tick-infested areas and early removal of attached ticks remain the most important prevention measures. There is a lower risk of infection if ticks are removed quickly, as infection generally does not occur during the first few hours of tick feeding.
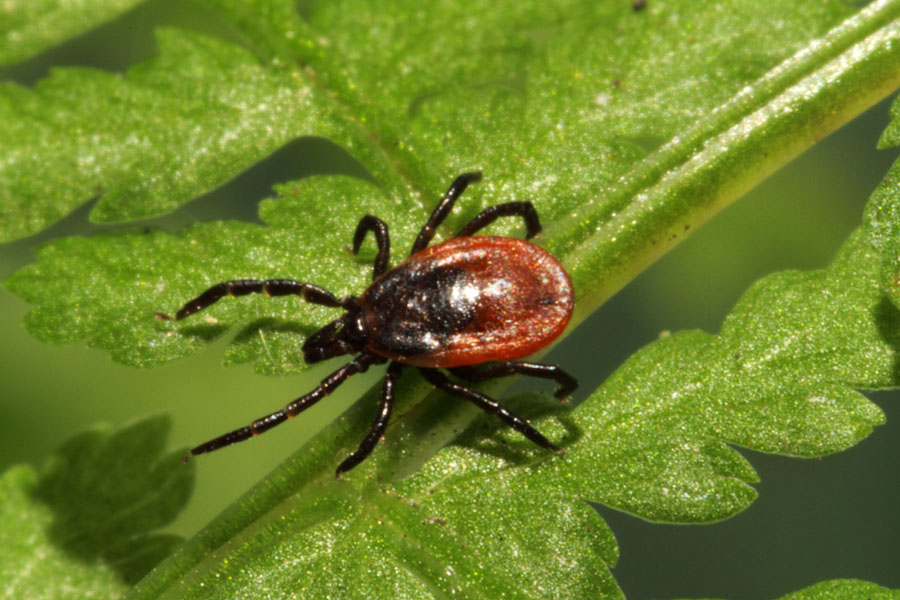

Ixodes Rinicus Tick
All over Europe
Tick-borne diseases can be found almost all over Europe, with some diseases being more prevalent in certain regions.
Inform yourself on areas where tick-borne diseases are present and ask your doctor regarding necessary precautionary measures before travelling to any of these areas, especially if you plan to engage in outdoors activities (camping, hiking, hunting, lake or river fishing, etc.) during your visit that might increase your exposure to ticks.
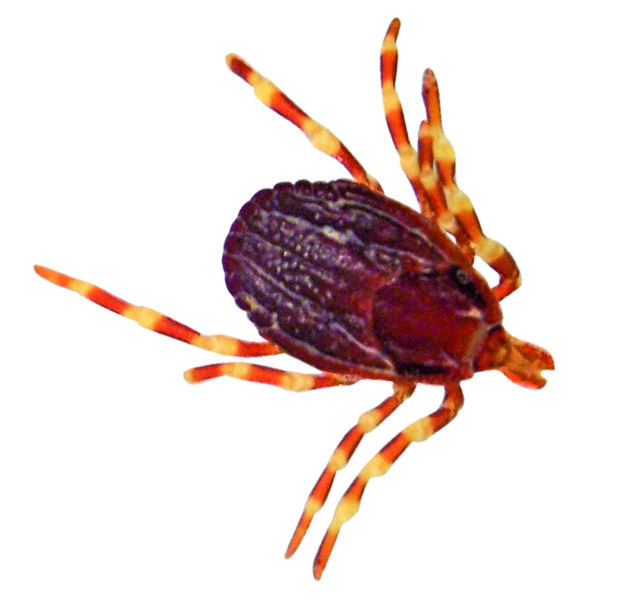

Hyalomma marginatum tick
For more information on tick-borne diseases please visit: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/tick-borne-diseases







Recent Comments